
The plenary session of the 2021 Global Mayors' Forum was held in Guangzhou On November 11. Zhong Nanshan, renowned respiratory expert, recipient of the Medal of the Republic and academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, gave a feature presentation at the conference.
He noted that the guiding principle of China's pandemic policy is life first and strict control of the disease. At the same time, mayors across the world should consider how to balance economy and pandemic control, "targeted prevention and control is important, but it cannot be escalated excessively, otherwise the economy will be affected".
Zhong Nanshan gave two groups of latest data: now 75.8% of the people in China have been fully vaccinated; and in Guangzhou, the proportion is 92.7%. "We should continue with the vaccination as it's a key safeguard measure".
The second data is the study on the immune persistence after the 3rd dose. The GMT increases quickly after the 3rd shot but will still decline after six months. Even so, the declined GMT remains higher than the level after the 2nd dose, proving the effectiveness of the 3rd one.

The following is the transcript of the full speech:
I am very pleased to participate in the 2021 Global Mayors' Forum and share the experience and practice of China, especially Guangzhou, in fighting the COVID-19 outbreak.

The is the data of the day before yesterday: Globally, there have been more than 250 million confirmed cases, including over 5 million deaths, and counting. What should we do?

This is in Wuhan last year when the National High Class Expert Committee announced to the public definite human-to-human transmission of the novel coronavirus and the infection of medical staff. Hence the question was posed to China: which way should we take? One way is suppression; the other is mitigation.
We should understand that outbreak is inevitable, but we need to find ways to control the incidence rate, which could be possible when medical services are sound. But the problem with COVID- 19 is that it is highly contagious. Its infection rate is higher than that of Sars and Mers. It spreads fast, so this path does not work very well.
18 years ago, Guangzhou had a painful experience - Sars, which posed serious impact to the society, when the once crowded streets were empty. This was a profound lesson that mitigation might prove not enough in the face of such a pandemic. Then what should we do?
China's leaders have an underlying principle - Life Supremacy. In this case, that means strong suppression of the disease. In China, life is above everything else, so that's the road we are going down.
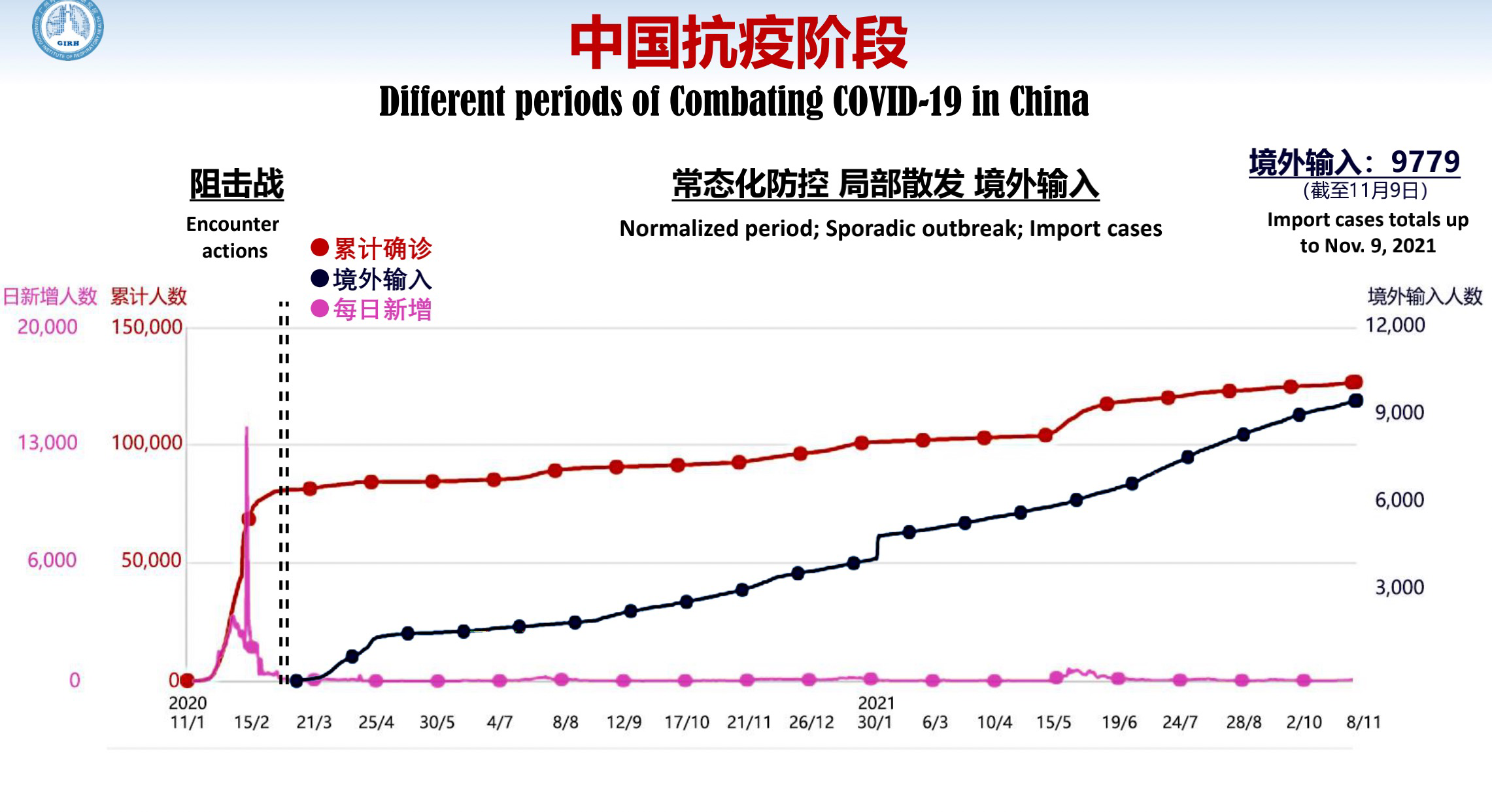
Let's look back on the overall dynamics of the COVID-19 in China from last January to now. The vertical coordinate refers to the number of people and the horizontal coordinate is the time, so we've had it under control after the peak in March. In the initial stage of the pandemic, the number of cases hit more than 80,000; but in the following 20 months, cases only increased 40,000. Some countries have seen more than 100,000 new cases a day. In China, the number of cases did climb, but over a long time, allowing us the window to restart the economy.

The WHO has summarized 4 strategies in combating COVID-19 by different countries: Aggressive containment aiming for zero community transmission, suppression, mitigation and no substantive strategy. Looking at it now, strong control and suppression are effective.
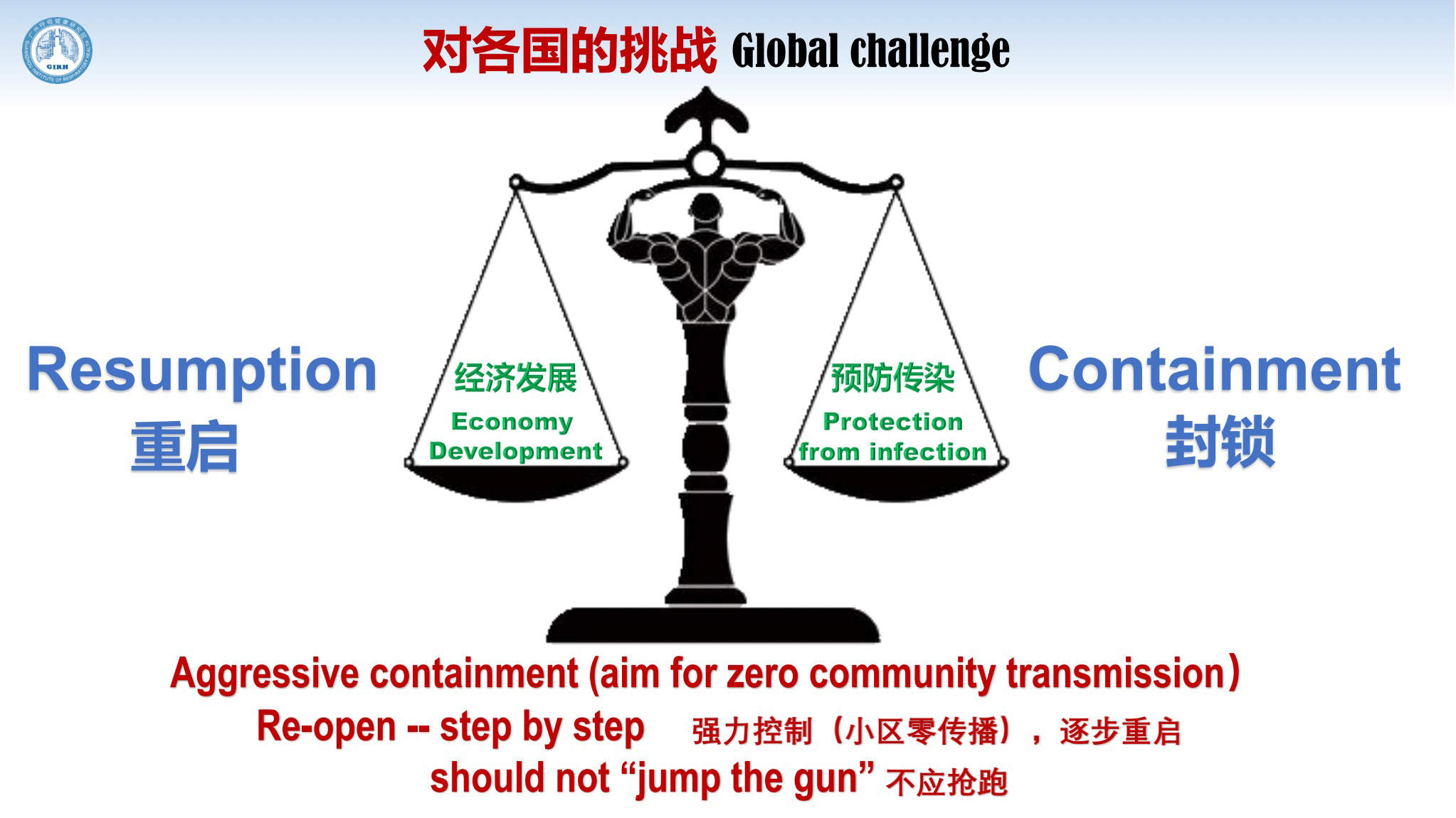
Mayors of cities around the world have to think about how to balance economic resumption and containment measures, and we have to figure out how to do both. Targeted prevention and control are important, however, my view is that you can't escalate the measures excessively as that will harm the economy.
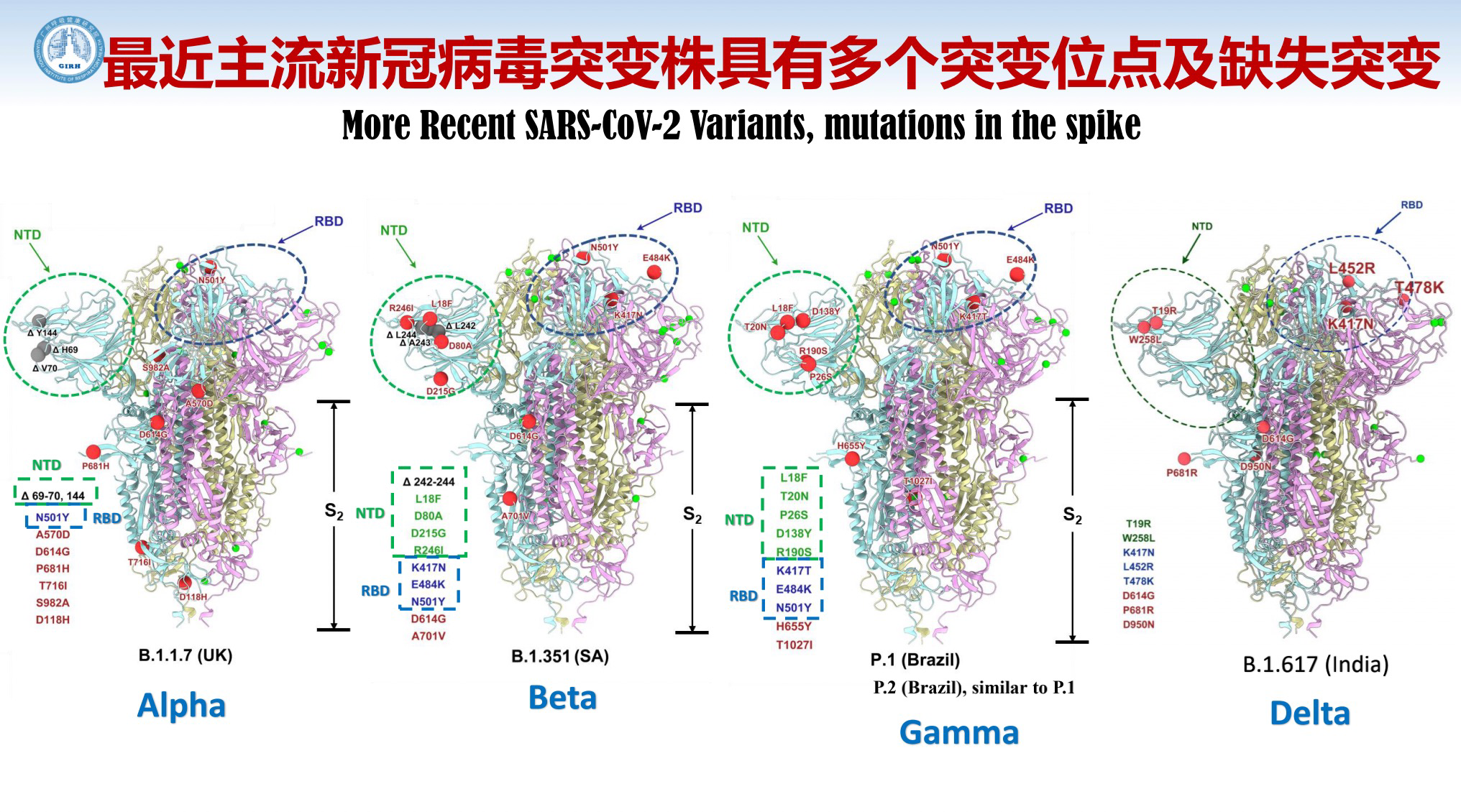
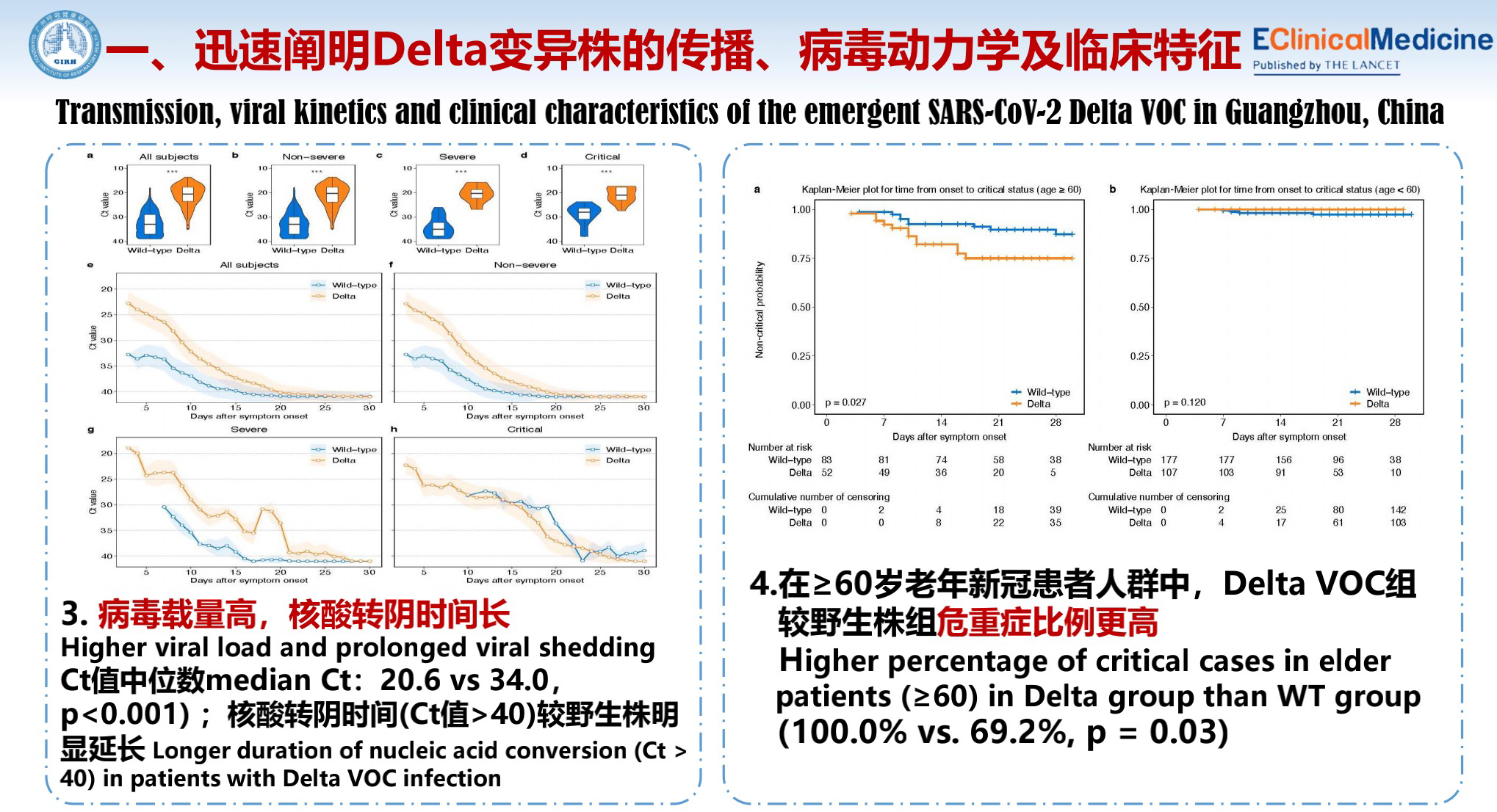
Let's look at the characteristics of the Delta variant infection and its prevention. The mutant strain has multiple mutation loci and therefore spreads easily.
Guangzhou had the first Delta variant community infection in China, which occurred on May 21 and ended on June 18, with 159 people infected. All cases received the second generation sequential analysis, and the results indicate high homology.

What are the characteristics of this outbreak? First, it spreads very quickly, with a clear transmission chain. Second, the incubation period is very short compared to the incubation period of the normal novel coronavirus. Delta VOC can spread to 5 generations within 10 days.
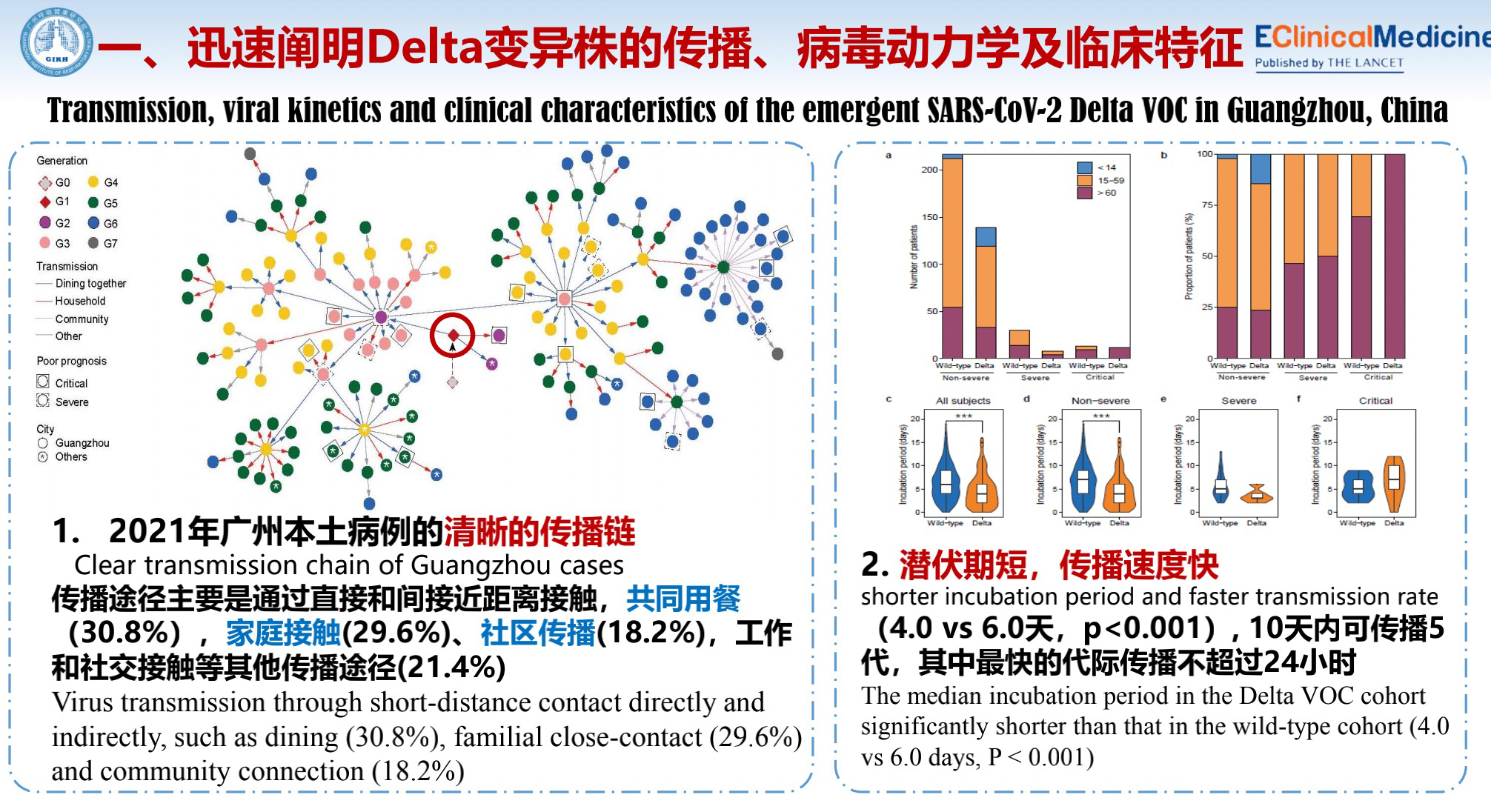
Third, the viral nucleic acid load in the patient's body is very high, and the viral shedding period is long. Fourth, the elder patients have a higher percentage of critical cases.
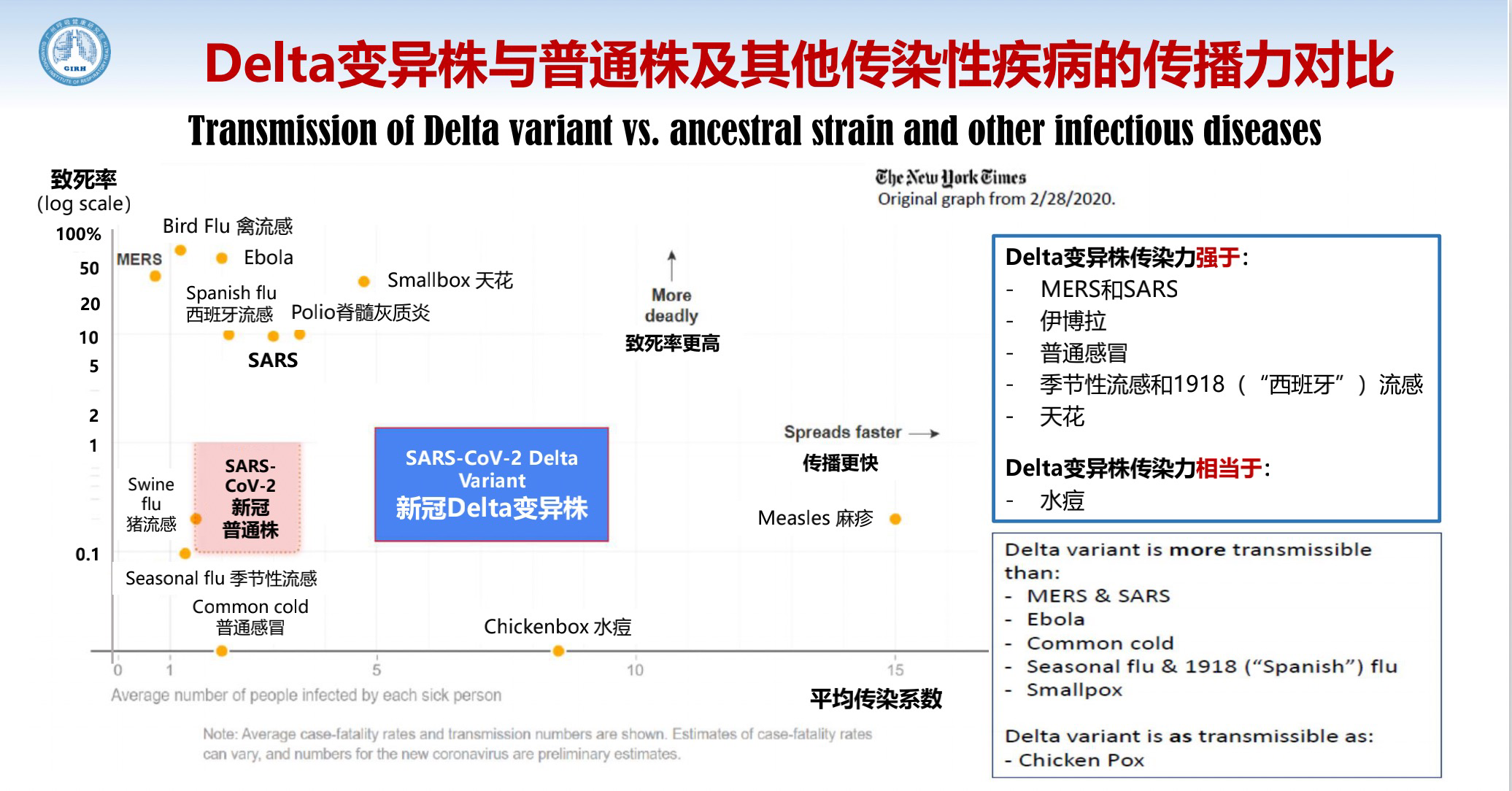
Let's compare the transmission of the Delta variant with that of the ancestral strain and other infectious diseases. The vertical coordinate refers to the fatality rate and the horizontal coordinate is the average transmission coefficient. The fatality rate of SARS-CoV-2 is 0.1%, and the spread is not particularly fast; the spread of its Delta variant is fast, and its mortality rate is as high as that of the ancestral strain. The Delta variant is somewhat as transmissible as chicken pox and smallpox, only the smallpox has a much higher mortality rate.
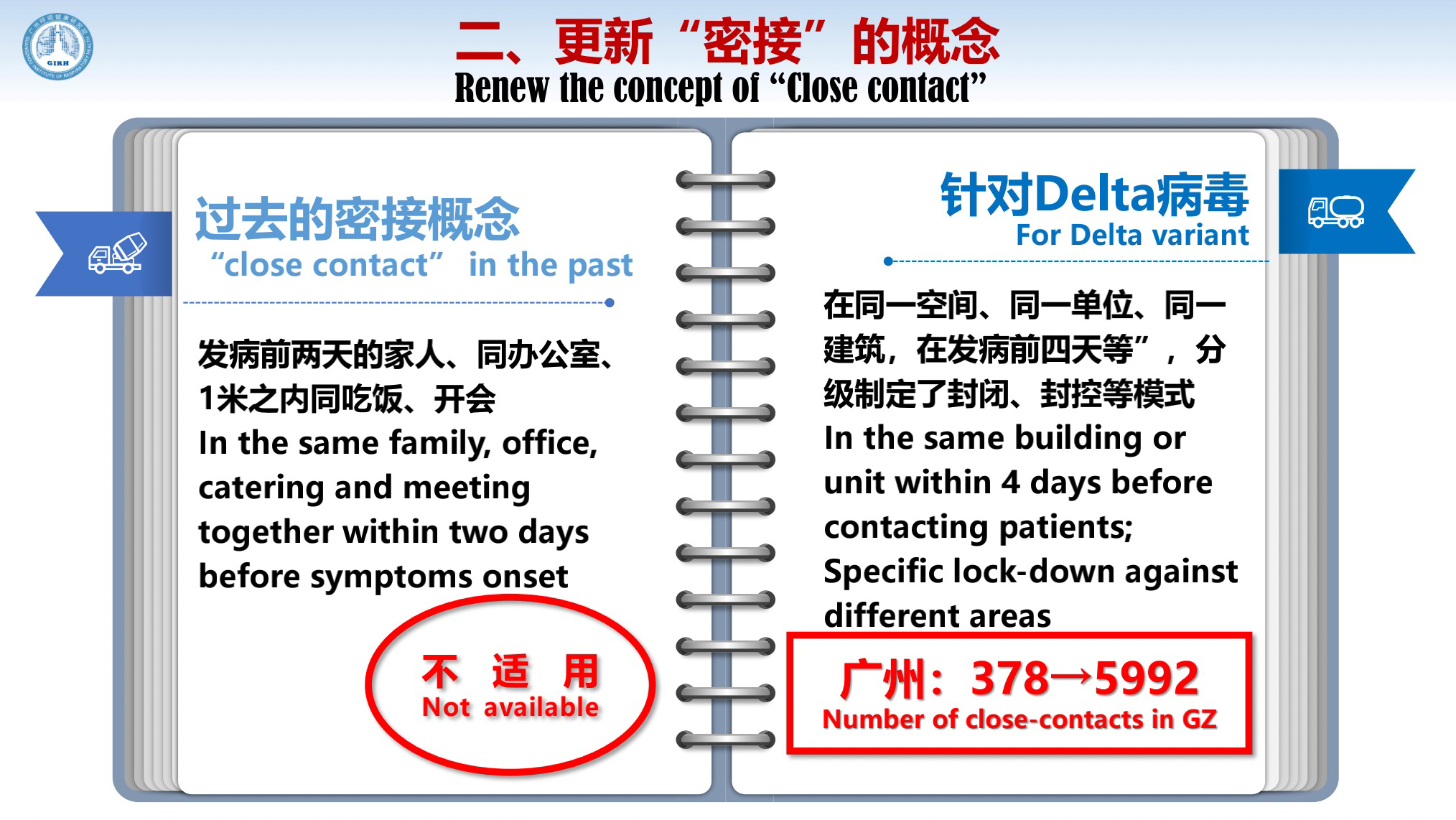
So what did Guangzhou do? We first renewed the concept of "close contract". In the past, "close contacts" are people "in the same family, office, catering and meeting together within 1 meter to each other within two days before the symptoms onset". For Delta variant, "close contacts" are those "in the same building or unit within 4 days before contacting patients", and we carried out specific lock-down against different areas.
According to the past definition, the number of close contacts was 378; but according to the new concept, the number increased to more than 5900.
Second, we innovated the yellow code regulation. As long as people have been to specific places, that can be tracked and their health codes will turn yellow, indicating they should take the nucleic acid testing as soon as possible. In this way, we have found some missed close contacts.

Third is the massive and rapid nucleic acid screening. This is the make-shift laboratory we built with transparent plastic, which allowed Guangzhou to achieve rapid full screening in some areas.

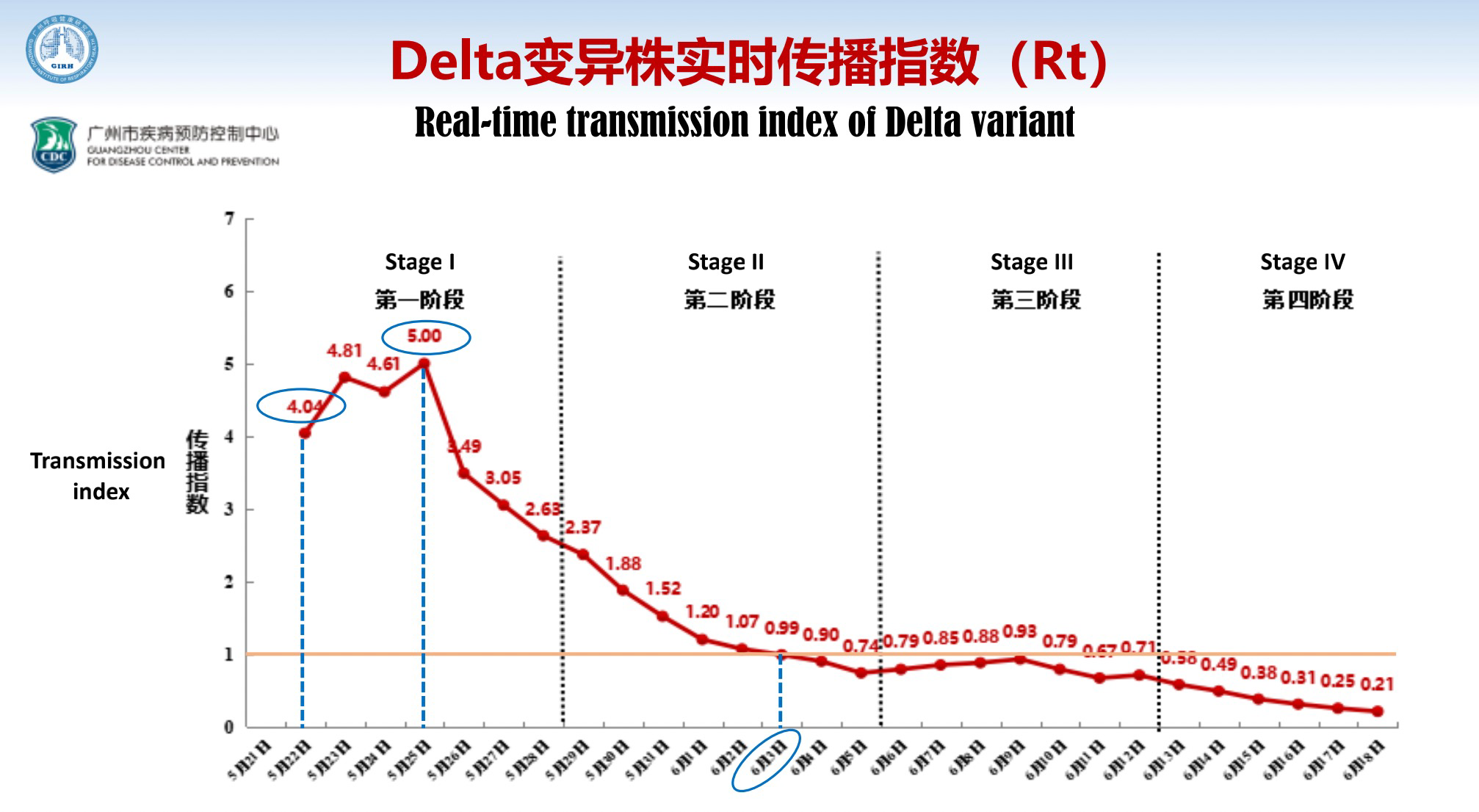
Through these measures, the real-time transmission index of the Delta variant in Guangzhou came down day by day.
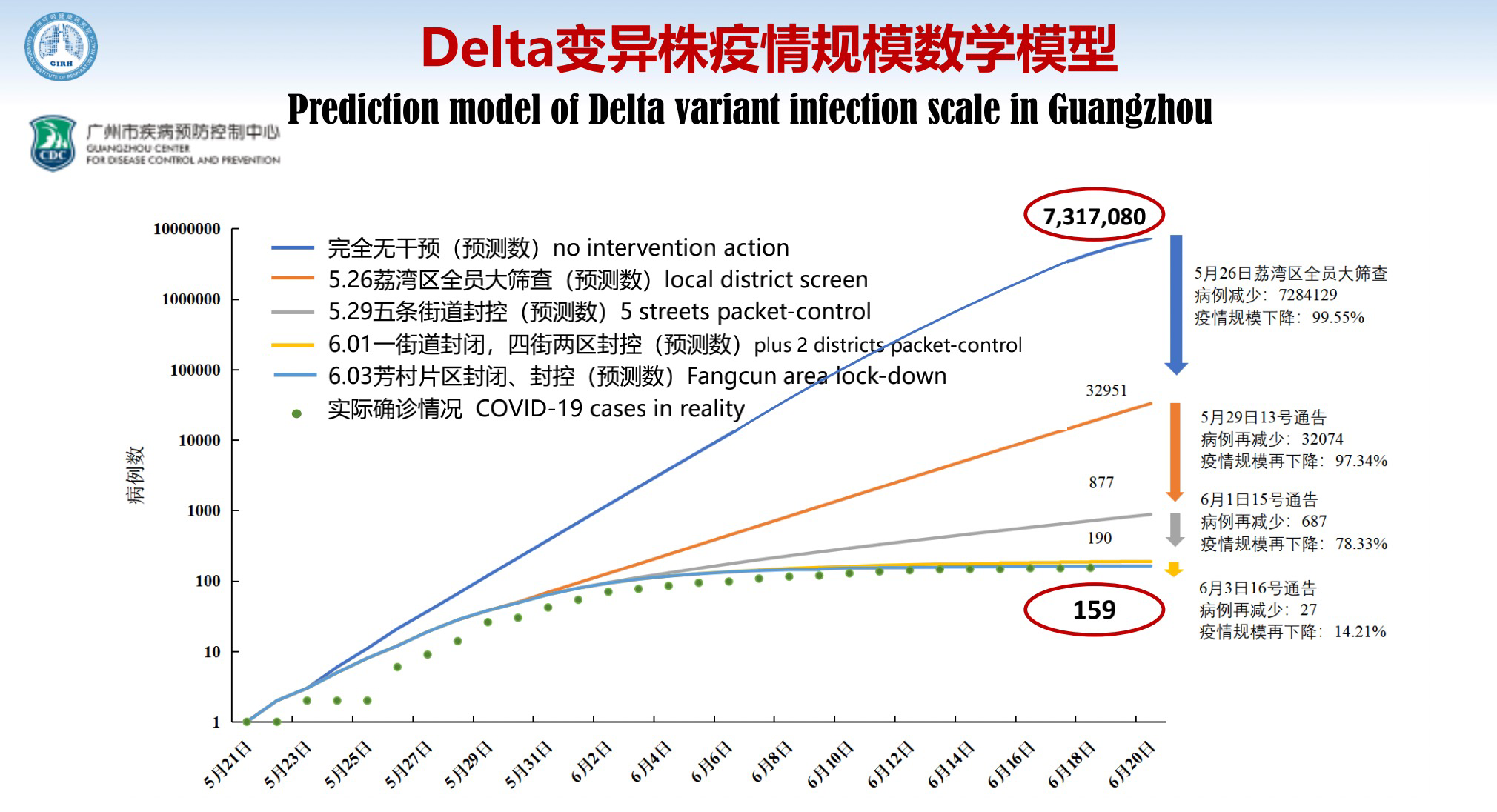
A prediction model shows that if Guangzhou took no intervention action, 7.3 million people would have been infected by June 20; but through our efforts, the actual number of cases is 159. This shows Guangzhou did a good job in strict and targeted containment.
When outbreak occurred at Nanjing Lukou International Airport, Guangzhou's yellow code system was also adopted and the transmission was effectively curbed. The duration of the community transmission was 24 days.

At present, there are still cases in Northwest China, Heilongjiang, and Dalian, Liaoning. This round of domestic outbreaks is also under targeted tracking, prevention and control; we are still able to contain the epidemic within a limited range.
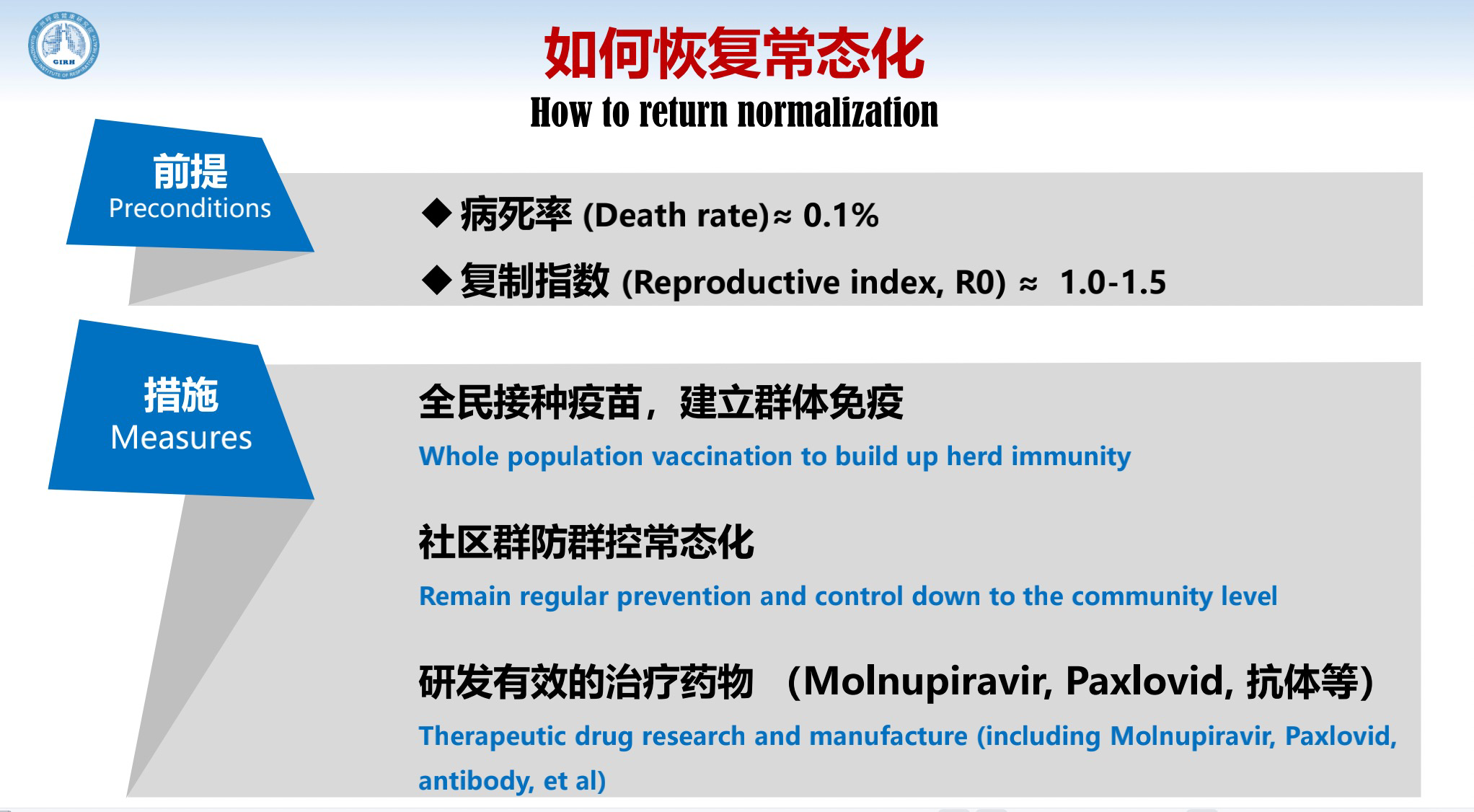
How to return to normalization quicker?
Under the preconditions that both the death rate and reproductive index have dropped, three measures should be taken at the same time. First, carrying out whole population vaccination to build up herd immunity; second, remaining regular prevention and control down to the community level, but don't overdo it; and third, developing effective therapeutic drugs.
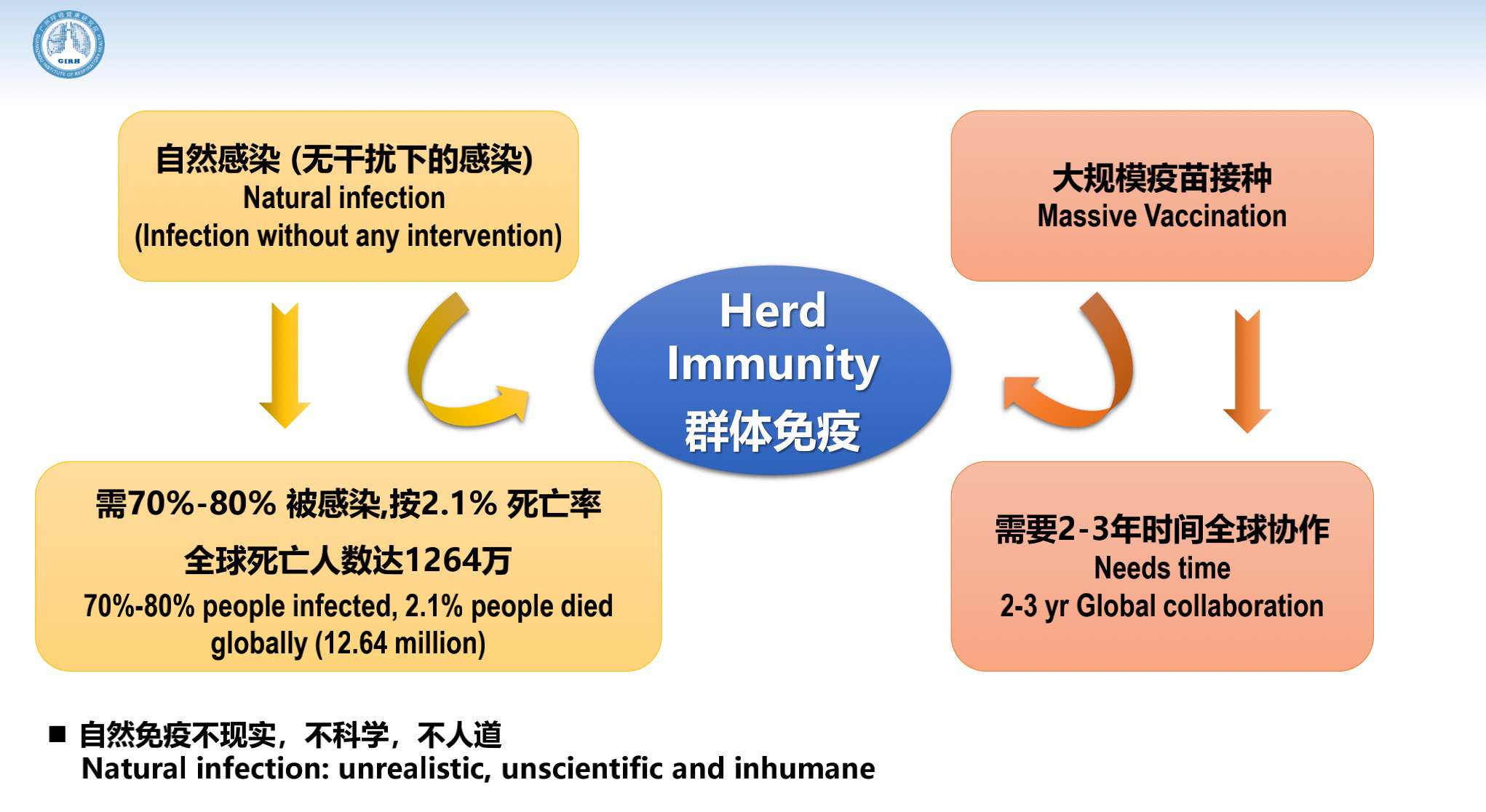
Natural herd immunity is unrealistic, unscientific and inhumane. At a 2.1% mortality rate, the global death toll would be 12.64 million.
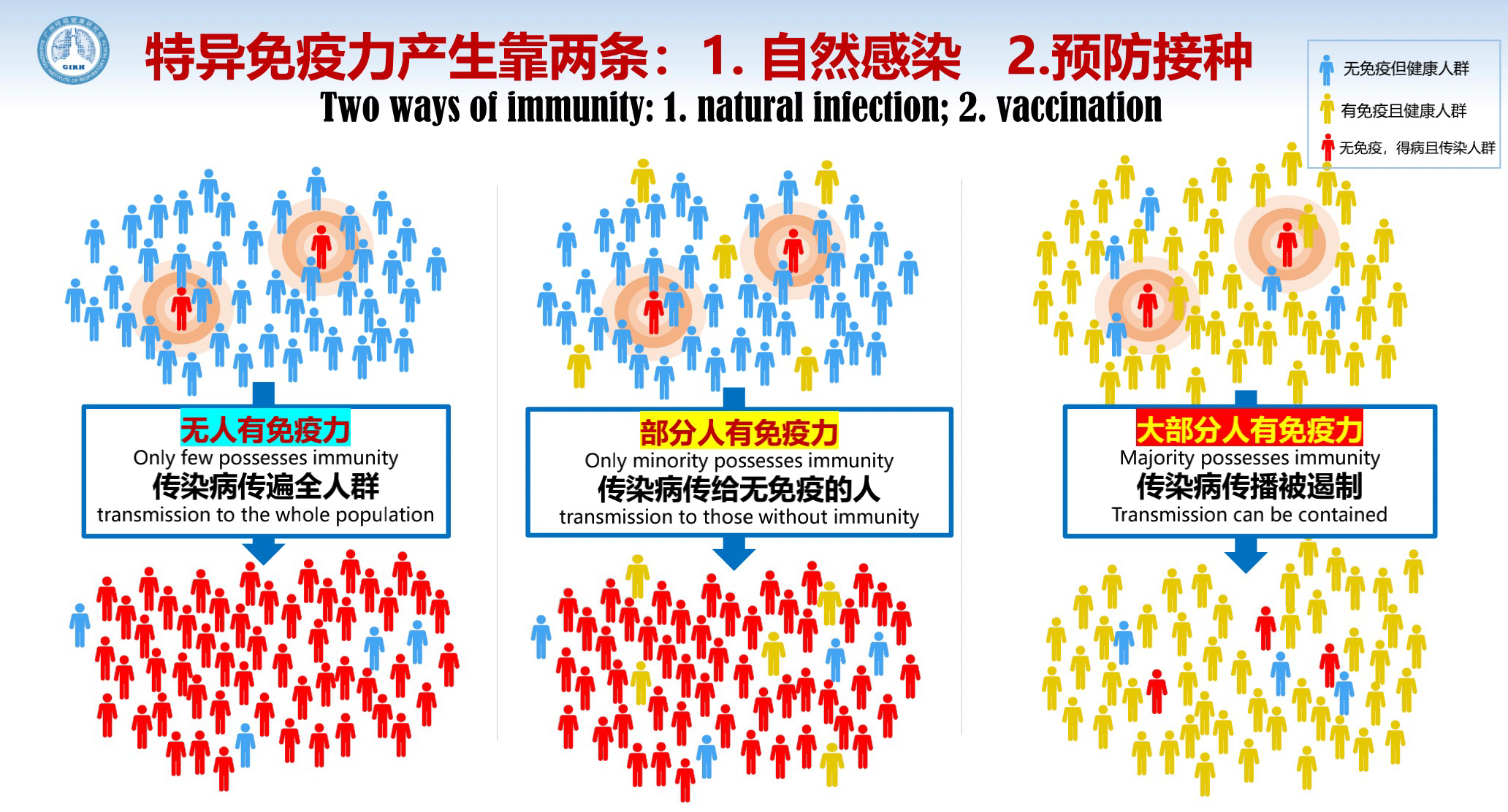
Specific immunity develops in two ways: natural infection and vaccination. When most people possess immunity, the transmission of infectious diseases can be contained.
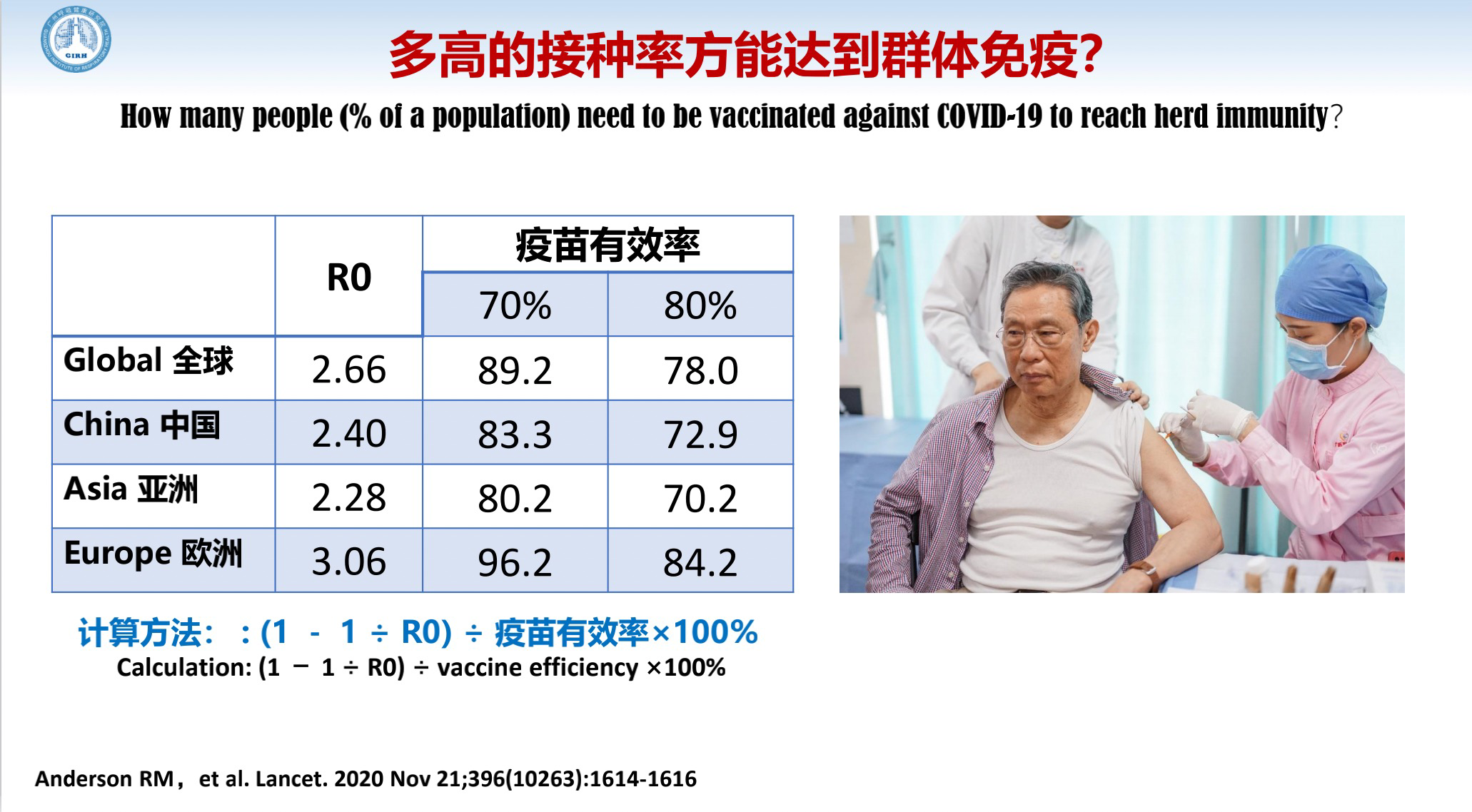
The present vaccine efficiency is 70% to 80%, so to reach herd immunity, more than 80% of the population must be vaccinated.
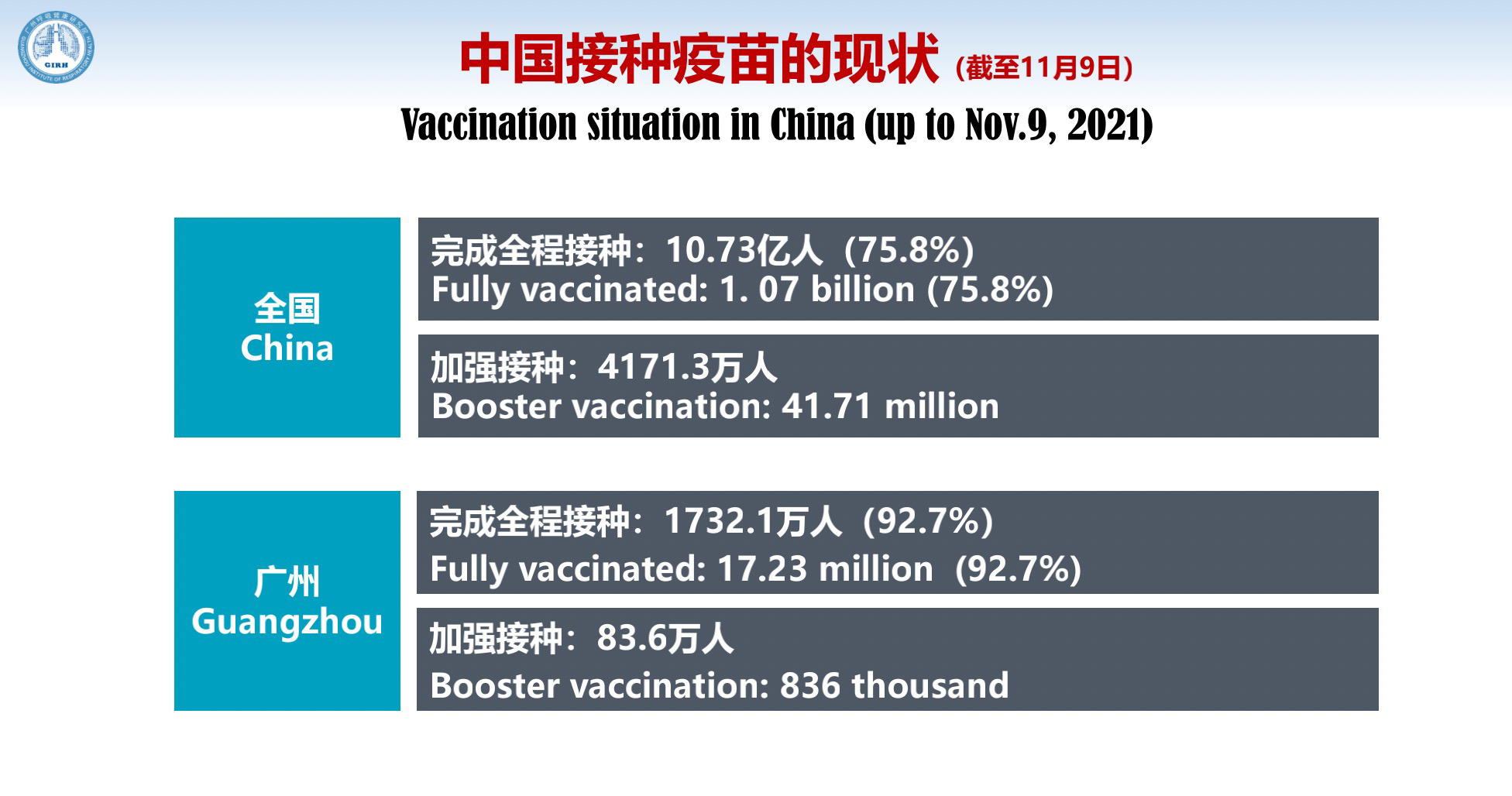
Data up to the day before yesterday showed that 75.8% of the population in China, that is, 1.073 billion people, have been fully vaccinated. More than 40 million people have taken the booster vaccination. In Guangzhou, by the day before yesterday, 92.7% of the population have been fully vaccinated, and more than 800,000 people have received the booster vaccination. We should continue to expand vaccination coverage as this provides important protection.

Currently 13 Chinese vaccines have reached phase III clinical trials, some have passed.
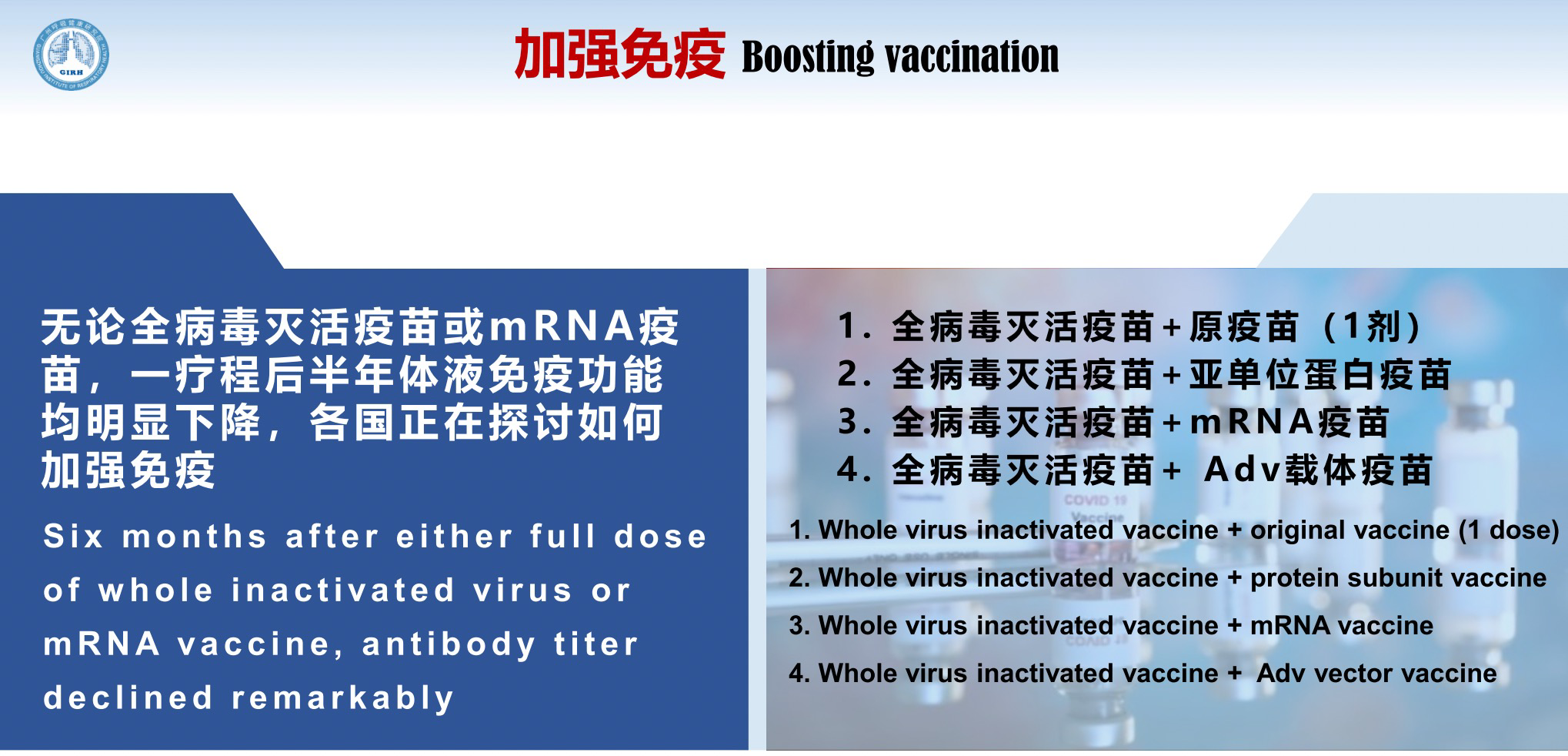
Study in Israel showed a sharp decline in the vaccine's protection effect after six months, with a rapid rebound of new cases. Six months after either full dose of whole inactivated virus or the mRNA vaccine, antibody titer declined remarkably. Countries are exploring ways to booster immunization.
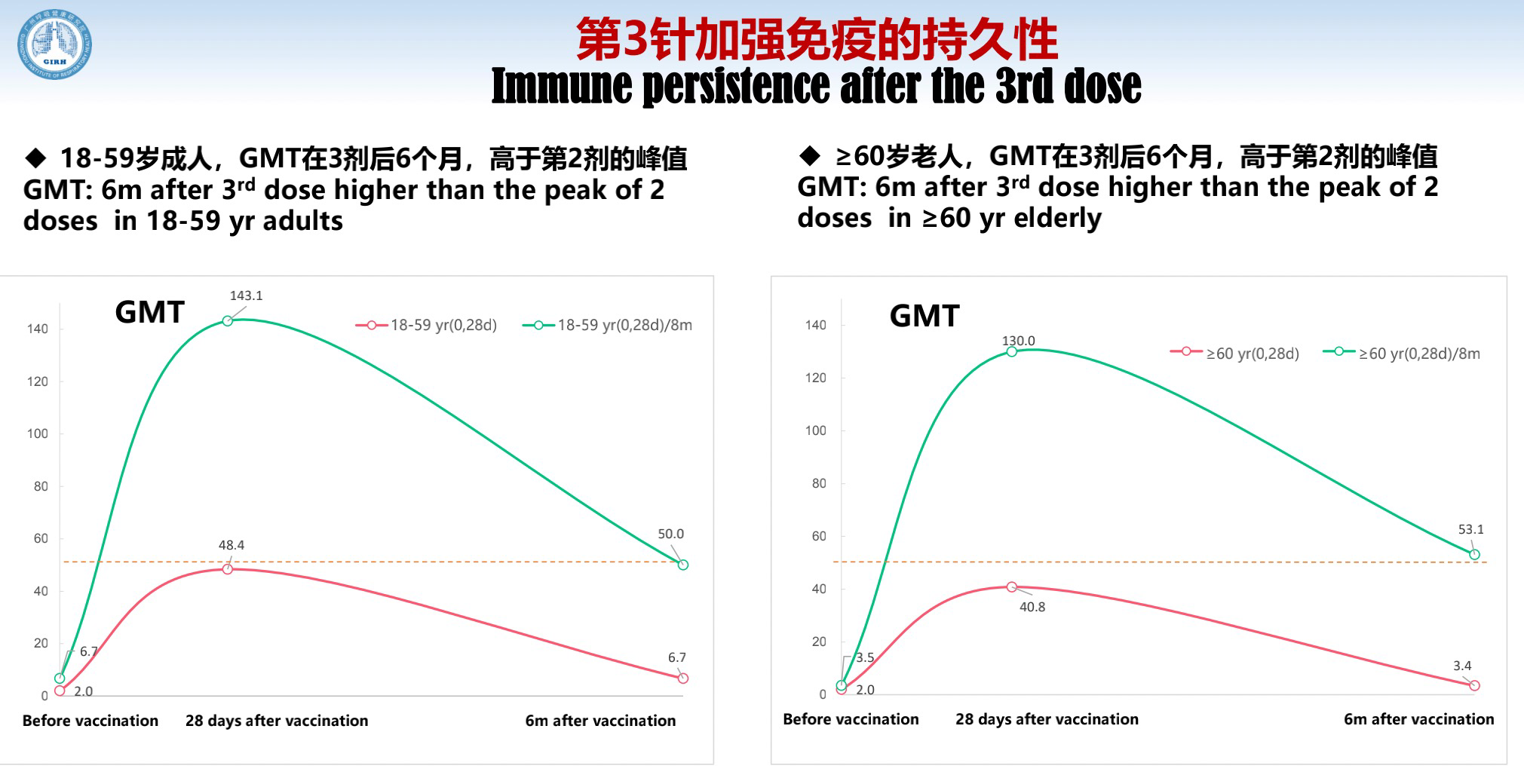
I have just received data from the study on the immune persistence after the 3rd dose. Antibodies increase rapidly after the 3rd dose, but they will still decline after six months. How is the decline? The study on both elderly people and children shows that after six months, their GMTs are about the same level as the peaks of 2 doses. So the 3rd dose is necessary.
Lastly, I want to say: No country is safe until all countries are safe! This is most important.
Reported by Huang Rongfang, Fang Qing/Guangzhou Daily
Edited by Lv Yun